Home
My name is Samuel Kroger, I am an assistant professor of Data Science & Analytics at Austin College. I gradutaed with a PhD in Computational Applied Mathematics & Operations Research (CMOR) at Rice University in 2024. I received my MA of Computational applied Mathematics and Operations research from Rice University in 2022 and a BA in Mathematics from Bates college in 2019. My primary research interest is the intersection of mixed integer programming, graph theory and combinatorics.
On this website you will find, publications, teaching experience, and my research projects explained below.

Thanks for visiting my website, feel free to reach out to me at sakroger@rice.edu with any questions.
Congressional districting
The United States House of Representatives is designed to represent the American population in politics. In order to achieve this each state is partitioned into parts who elect politicians to represent them in the House of Representatives. There is a lot of discussion about the fairness of these maps. In this work we use mixed integer programming to come up with feasible maps that explore the representation of minority populations.
Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act calls for the creation of majority-minority districts to provide minority groups with opportunities to elect representative of their choice. These majority-minority districts must satisfy three conditions:
-
Compactness and numerosity,
-
Political cohesion,
-
Sufficiency of majority vote to defeat the preferred candidate of minorities.
In this work we aim to produce viable maps which include these majority-minority districts.
A fixing Algorithm for the Maximum Cardinality Independent set Problem
An independent set I, is a subset of a graph G such that the subgraph induced by I (i.e., G[i]) has no edges.
The maximum cardinality independent set problem(MCIP), seeks a independent set I with largest cardinality.
This is a well studied problem with a ray of applications spanning, chemistry, genetics, coding theory, graph coloring, and covering problems.
In this work we propose a polynomial time algorithm which can fix simplicial vertices for the MCIP.
This algorithm recursively fixes certain simplicial vertices and their neighbors to solve the MCIP more efficiently.
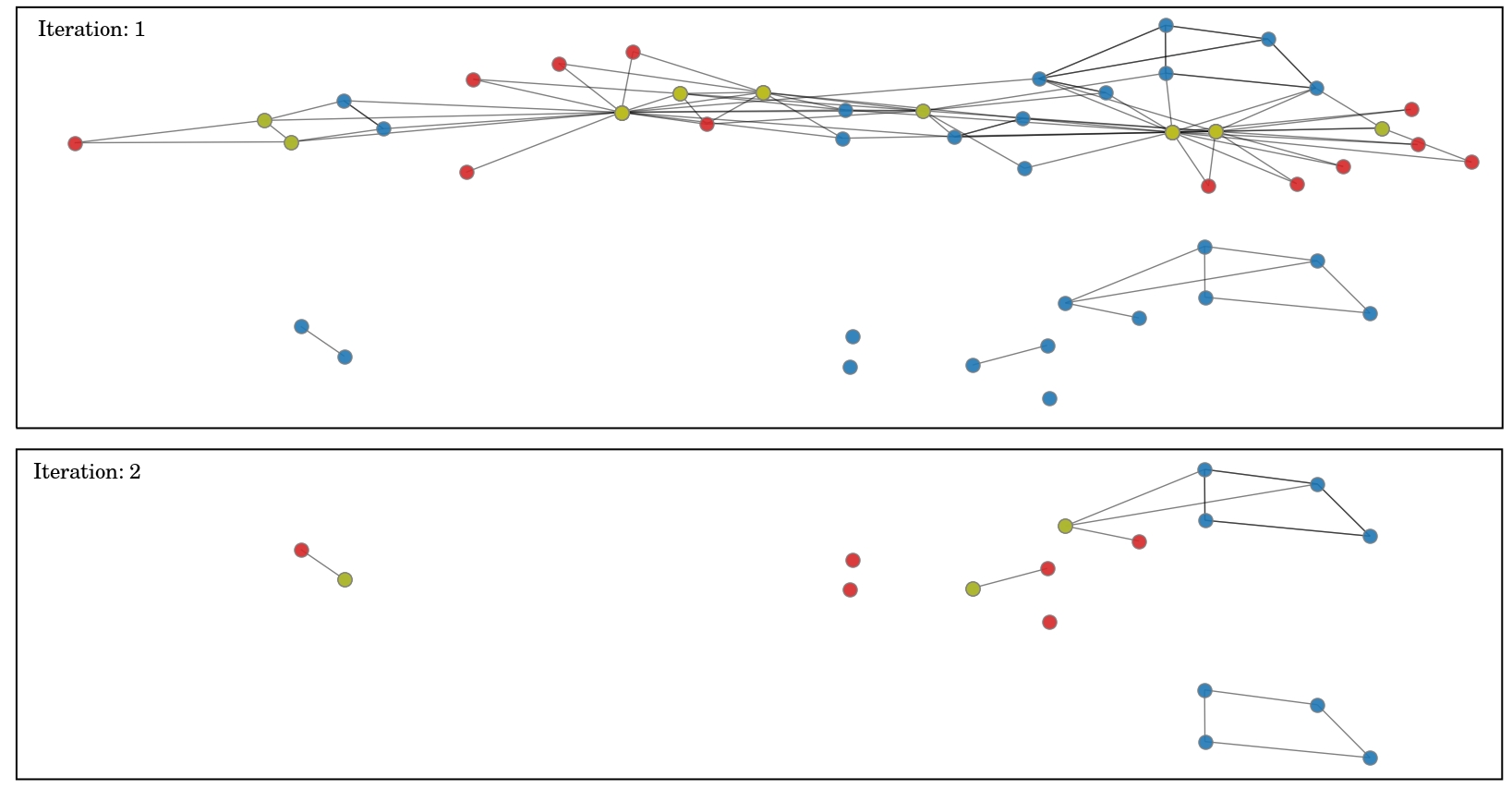
Below is an image showing how our polynomial time algorithm can prune the karate graph into only four nodes. The red vertices are simplicial nodes, the yellow vertices are neighbors of simplicial vertices, and the blue vertices are the remaining vertices.
Maximum Anchored k-core
The k-core of a graph is the maximal subgraph in which each vertex has degree at least k.
We study an extension of this problem with an additional budget parameter b.
Given a simple finite graph G(V, E) and parameters k and b, we seek a largest subset of vertices S such that S induces a subgraph in which at most |V| - b have degree at least k.
Solving this problem is vital to the vitality of social networks.
Below is an optimal solution to the anchored 4 core with budget five on the karate graph.